Inorganic open framework based on lanthanide ions and polyoxometalates with high proton conductivity†
Abstract
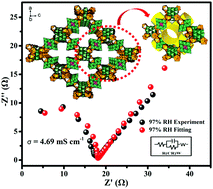
The development of new proton-conducting materials that are cost effective and have high proton conductivity and water stability is very important in fuel cell technology. Lanthanide-based metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) exhibit proton conduction properties but usually display the problem of poor hydrophilicity. We propose that the organic ligands can be replaced with polyoxometalates, and the as-prepared lanthanide-based inorganic porous materials with lanthanide ions may possess improved hydrophilicity and proton conductivity. Herein, we re-synthesize two inorganic open frameworks based on [MnV13O38]7− clusters and lanthanide ions (H[Ln(H2O)4]2[MnV13O38]·9NMP·17H2O (Ln = Ce (1), and La (2); NMP = N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone)) and explore their potential proton conductivities. Under the same test conditions, both compounds show only a little difference in proton conductivities with the values of 4.68 × 10−3 S cm−1 and 3.46 × 10−3 S cm−1 at 61 °C, respectively, which are much higher than those of the previously reported proton-conducting materials based on lanthanide metal ions. In addition, we also prove their proton-conducting nature by measuring the electron resistance via the Hebb–Wagner polarization technique and proton conduction via the D2O-exchange test. The 3D channel in the two compounds plays a key role in constructing an efficient proton transfer pathway via a hydrogen bonding network.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...