Sustainable development of a surface-functionalized mesoporous aluminosilicate with ultra-high ion exchange efficiency†
Abstract
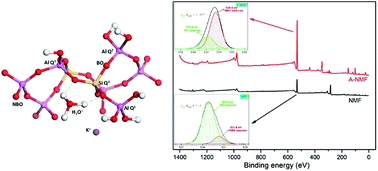
The present work employs a facile hydroxylation technique to efficiently functionalize the surface of a waste-derived aluminosilicate for ultra-high heavy metal uptake via ion exchange. The functionalization process leads to the transformation of a nonporous hydrophobic waste material to a mesoporous hydrophilic material with a high concentration of ion exchange sites. The modification of the surface and textural characteristics of the mesoporous aluminosilicate has been thoroughly elucidated. The functionalization brings about the partial depolymerization of the aluminosilicate network and the transformation of unreactive bridging oxygens (BO) into non-bridging oxygens (NBO) as active sites as evidenced by 29Si NMR and FTIR. The positively-charged alkali metals bound to the NBO act as facile ion exchange sites. Ultra-high heavy metal uptake capacity of the functionalized material through a combination of ion exchange and physisorption mechanisms has revealed the great potential of this aluminosilicate material for treatment of heavy metal-laden wastewater in a sustainable manner for practical applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...