Hydrogen-bonded supramolecular micelle-mediated drug delivery enhances the efficacy and safety of cancer chemotherapy†
Abstract
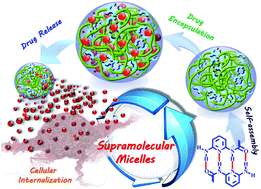
Water-soluble supramolecular polymers can be created by incorporation of self-complementary multiple hydrogen bonding groups. However, technically simple fabrication of water-soluble supramolecular polymers with highly desirable physical properties—to achieve micelles suitable for effective delivery of drugs for cancer treatment—remains a significant challenge. We developed a new polyethylene glycol-based supramolecular polymer containing self-complementary quadruple hydrogen bonding groups, which spontaneously assembles into nanospherical micelles in an aqueous environment. These supramolecular micelles can be readily controlled to obtain the desired structural stability and possess excellent pH-responsive and drug-loading capabilities, as well as good biocompatibility towards both normal and cancer cells. The resulting drug-loaded micelles exhibit tunable drug loading capacity and excellent long-term drug-entrapment stability due to the strong affinity between the drug and micelle core, which led to highly efficient drug loading. In addition, in vitro release assays indicated the drug-loaded micelles can be triggered to rapidly release the drug under mildly acidic conditions. More importantly, fluorescence microscopy and flow cytometry clearly demonstrated that drug-loaded micelles were effectively endocytosed by cancer cells and induced apoptosis; therefore, this newly developed supramolecular system could serve as versatile drug nanovehicle for safe, effective controlled drug release to achieve superior chemotherapeutic effects.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...