Maximizing macromonomer content produced by starved-feed high temperature acrylate/methacrylate semi-batch polymerization†
Abstract
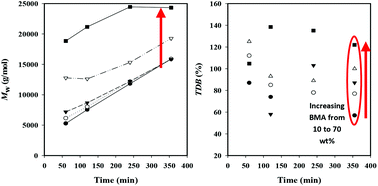
Butyl acrylate and butyl methacrylate high-temperature starved-feed solution semi-batch copolymerizations with varying monomer feed composition, final polymer content, and reaction temperature were carried out to investigate the impact of operating conditions and secondary reactions on product molecular weight (MW) and terminal double bond (TDB) content. Both quantities are increased by lowering initiator level; while increasing the final polymer content also increases MW by promoting branching in BA homopolymerization, it lowers the fraction of TDB in the product. The results can be understood by considering the formation and consumption of both the midchain radicals (MCR, formed by acrylate backbiting) and the macromonomer product formed by β-scission of MCRs favored under low monomer higher temperature conditions. For BA homopolymerization, the highest TDB level that could be achieved was ∼70%, with this level increased to >90% by adding butyl methacrylate (BMA) as a comonomer, as the fragmentation probability of the MCR is increased when BMA is the adjacent monomer unit.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...