Encapsulating an organic phase change material within emulsion-templated poly(urethane urea)s†
Abstract
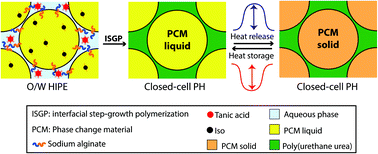
PolyHIPEs (PHs) are usually porous polymer monoliths templated within high internal phase emulsions (HIPEs), emulsions containing at least 74% dispersed internal phase, through free radical polymerization. Truly closed-cell PHs for encapsulating water, aqueous solutions, or inorganic salts have been synthesized within water-in-oil HIPEs through a judicious selection of HIPE formation and polymerization conditions. Encapsulating organic phase change materials such as octadecane (OD), within PHs would be advantageous for thermal energy storage and release applications. Here, exceptionally large amounts (∼90 wt%) of OD were encapsulated as micrometer-scale capsules within poly(urethane urea) (PUU) PHs that were synthesized within oil-in-water HIPEs via interfacial step growth polymerization. The PUU was based on tannic acid (polyol) and sodium alginate (reactive surfactant), both in the aqueous external phase, and an isocyanate in the organic internal phase. The PH synthesized using hexamethylene diisocyanate (HDI), exhibited a relatively high thermal energy storage capacity (211 J gsample−1), a thermal behavior that was significantly different from that of OD, and robust mechanical behavior. It is the more flexible macromolecular structure produced with HDI that enables the successful encapsulation of the OD and the associated efficient thermal energy storage and robust mechanical behavior.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...