Antibacterial activities of N-alkyl imidazolium-based poly(ionic liquid) nanoparticles†
Abstract
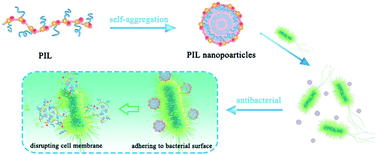
Poly(ionic liquid)s (PILs) can self-assemble into polymeric nanoparticles with highly ordered inner structures, which make them potential candidates for antibacterial agents because of their highly concentrated local charges. However, investigation of the antibacterial application of self-assembled PIL nanoparticles has seldom been carried out. Here, alkyl imidazolium-based PILs were synthesized via a simple free radical polymerization and the antibacterial activities of the corresponding PIL nanoparticles were systemically investigated. These obtained PIL nanoparticles exhibited excellent antibacterial activities against both Escherichia coli (E. coli) and Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus). There was a clear dependence of antibacterial efficacy on the alkyl chain length, namely C12 > C16 > C10 > C8, implying that an optimum alkyl chain length is needed to disrupt the cell membrane. In particular, the contribution of the hydrophobicity effect and charge effect to antibacterial efficacy was evaluated by introducing negatively charged units into PILs. The hydrophobicity effect was shown to be more profound than the charge effect. In addition, the synergistic effect of anions was also found to be dependent on the alkyl chain length of PILs. The proposed structure-antibacterial activity relationship is of vital importance for the structure design and property optimization of antibacterial polymer nanoparticles.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...