An ionic liquid crystal-based solid polymer electrolyte with desirable ion-conducting channels for superior performance ambient-temperature lithium batteries†
Abstract
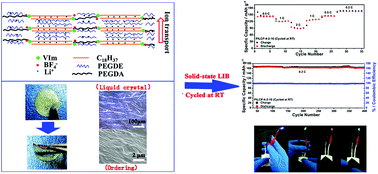
Almost all the traditional ionic liquids lack liquid crystal properties. Only a small number of ionic liquids show liquid crystal properties, which can be named as ionic liquid crystals (ILCs). The liquid crystal characteristics of ILCs endow them with good ordering. More specifically, the ILC macroscopic alignment of phase-segregated ordered nanostructures can be considered as ion pathways and further fixed by photopolymerization to fabricate nanostructured ion-conductive electrolyte films. However, there are no reports using ILC-based solid polymer electrolytes (SPEs) for solid-state polymer lithium batteries (SSPLBs). Here, a free-standing and flexible SPE through photopolymerization of ILC/poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate/poly(ethylene glycol) dimethyl ether/LiBF4 for SSPLBs was first designed and then successfully prepared. The as-obtained ILC-based SPE exhibits superior comprehensive electrochemical properties in terms of high ionic conductivity (1.96 × 10−4 S cm−1, 30 °C) and a wide electrochemical window (5.2 V). Particularly, the SPE delivers a high transference number of Li+ (0.6) due to the construction of ion channels for efficient transport of Li+. More importantly, the SPE also shows good interface contact with electrodes and can effectively suppress the growth of lithium dendrites. Thus, ILC-based SPE LiFePO4/Li cells present excellent long cycling stability (the average discharge capacity is ∼164 mA h g−1 with coulombic efficiency close to 100% throughout 375 cycles at 0.2 C) and superior rate capability at room temperature. Even at 0 °C, the SSPLBs can run very well. Our study opens a new way for ILC-based SPE to be practically applied in SSPLBs and also provides major progress on addressing the challenges of room temperature/low temperature SSPLBs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...