A crown-ether-based moldable supramolecular gel with unusual mechanical properties and controllable electrical conductivity prepared by cation-mediated cross-linking†
Abstract
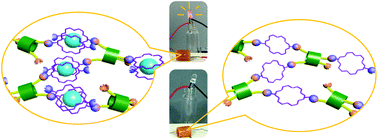
Typical supramolecular gels do not exhibit electrical conductivity because of the wide band gaps present in the low-conjugation gelator molecules and the long distances between them, which arise because of the large amount of solvent within gel networks. Consequently, the practical applications of supramolecular gels are largely limited. Herein, a strategy for significantly enhancing the mechanical, electrical, and vibrational isolation properties of supramolecular gels derived from low-molecular-weight building blocks, which involves the incorporation of Cs+ ions, is described. High-elasticity supramolecular gels produced from the hydrazone reaction between calix[4]arene- and 18-crown-6-ether-based building blocks are mechanically strong and can be molded into free-standing objects. By controlling the concentration of Cs+ in the supramolecular gels, their mechanical and electrical properties can be tuned. The supramolecular gels exhibit 34-fold and 62-fold enhanced storage and loss moduli, respectively, upon addition of Cs+ ions. Furthermore, the electrical conductivities of the supramolecular gels proportionally increase with the amount of Cs+ ions in the gel network. These dramatic enhancements are due to the sandwich complex formation between the 18-crown-6 moieties and Cs+ ions. Also, the supramolecular gels reveal effective vibration-isolation abilities. It is believed that this strategy presents new possibilities for developing soft materials with unique functions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...