Functionalization of polyfluorene-wrapped carbon nanotubes via copper-mediated azide–alkyne cycloaddition†
Abstract
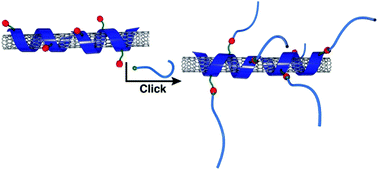
Developing methodologies that efficiently functionalize carbon nanotubes without damaging nanotube optoelectronic properties is an ongoing challenge. Here, we examine the scope of Copper-Mediated Azide–Alkyne Cycloaddition (CuAAC) for coupling an azide-containing polymer-nanotube complex with an alkyne-functionalized molecule. Various copper sources were screened, and reaction progress between the azide-containing polyfluorene and phenylacetylene was monitored by infrared spectroscopy via the disappearance of the polymer azide stretch at ∼2090 cm−1. It was found that Cu(OAc) was the only copper source that resulted in quantitative triazole formation, while copper halide salts were unable to afford complete conversion even at elevated temperatures. Reactive, noncovalently functionalized polymer-nanotube complexes were prepared using the polyfluorene with azide groups in its side chains. Upon reaction optimization, it was found that the reactive polymer-nanotube complexes could be coupled to phenylacetylene using Cu(OAc) under ambient conditions. To further evaluate the efficiency of CuAAC in derivatizing reactive polymer-nanotube complexes, a series of monomethyl ether polyethylene glycol (mPEG) polymers of varying molecular weights (Mn's from 0.75 to 41 kDa) were functionalized with alkynes using Steglich esterification. It was found that the polymer-nanotube complex was efficiently decorated with 41 kDa mPEG side chain grafts, without requiring an excess of alkyne-functionalized mPEG. Following the functionalization of the hydrophobic polymer-nanotube complex with mPEG, re-dispersion into aqueous solution was investigated and a minimum mPEG Mn of 2.0 kDa was found to be necessary to drastically alter dispersability. As evidenced by Raman spectroscopy, metal-mediated chemistry resulted in no damage to the nanotube sidewall. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy analysis indicated that some residual copper remained after washing with solvent.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...