Preparation of Pt(iv)-crosslinked polymer nanoparticles with an anti-detoxifying effect for enhanced anticancer therapy†
Abstract
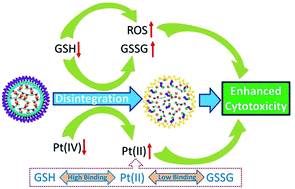
Cisplatin is a widely-used chemotherapeutic drug in the clinic against a range of cancers. However, its anti-cancer efficacy and bioavailability are severely affected by systemic toxicity as well as drug resistance, which are mainly due to indiscriminate body distribution, low tumor accumulation and glutathione (GSH)-related drug detoxification. In this study, we prepared for the first time a new kind of Pt(IV)-crosslinked polymer nanoparticle with small, uniform size and high loading of cisplatin (60.8%). Such a kind of polymer nanodrug could keep its structural integrity during blood circulation to afford higher tumor accumulation via the EPR effect and receptor-mediated targeting effect, yet rapidly self-disintegrate to release drugs in response to tumor intracellular bio-reducing molecules, such as glutathione (GSH), resulting in efficient cancer cell inhibition and reduced systemic toxicity in vivo. Meanwhile, some of the cellular GSH molecules are depleted and transformed into an oxidized GSSG form to decrease their chelating interaction with platinum drugs, which attenuate their detoxifying effect on the Pt(II) species and may have an advantage for overcoming the tumor resistance to cisplatin induced by GSH. Moreover, the maximum tolerated dose of drug could be greatly enhanced (>3 fold), which improved the bioavailability of the nanodrug at relatively high doses. The present work provides a novel drug self-crosslinked design tactic and might open a new window for clinical cancer treatment.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...