Hyperbranched PEG-based multi-NHS polymer and bioconjugation with BSA†
Abstract
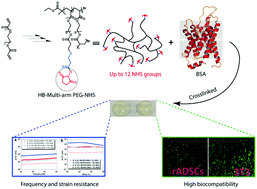
Star-shaped poly(ethylene glycol)-N-hydroxysuccinimide (star-PEG-NHS) has shown great promise in a variety of biomedical applications owing to its non-toxicity, innate non-immunogenic properties and versatile, multifunctional end groups. However, its complex and sophisticated synthetic methods, as well as high costs, have significantly impeded its wide application. Here, we report the design and synthesis of a hyperbranched PEG-based polymer with multiple NHS functional groups (>12). The hyperbranched PEG-based multi-NHS polymer can react easily with a protein (bovine serum albumin, BSA) to form a PEG-protein hydrogel that displays great potential for biomedical applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...