Thermo- and pH-responsive poly(ionic liquid) membranes†
Abstract
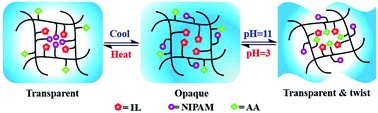
Thermo- and pH-responsive poly(ionic liquid) (PIL) membranes were synthesized via photo-crosslinking of imidazolium type IL monomers with acrylic acid (AA), N-isopropylacrylamide (NIPAM), and acrylonitrile (AN). The transmittance of the prepared PIL membranes was determined by the concentration of AA units and the hydrophobicity of PIL counter anions, and could be altered in response to temperature and (or) pH. The shape deformation of the PIL membranes can be reversibly tuned by changing the pH value of aqueous solutions or gas atmospheres (NH3/HCl). The dual-responsive PIL membranes prepared in this work can act as a soft actuator, and would have potential applications in advanced sensors and functional materials for inscription of information.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...