The synthesis and aqueous solution properties of sulfobutylbetaine (co)polymers: comparison of synthetic routes and tuneable upper critical solution temperatures†
Abstract
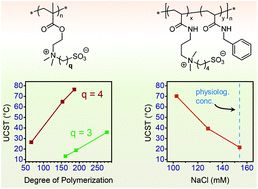
Polysulfobutylbetaine (SBB) (co)polymers, zwitterionic species bearing ammonium and sulfonate groups separated by a butyl spacer in every repeat unit, were prepared through three different synthetic routes and their aqueous solution behaviour was studied. Postpolymerization quaternization of poly[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate] with 1,4-butanesultone resulted in incomplete modification due to the low reactivity of this alkylating agent. RAFT radical polymerization of SBB-functional (meth)acrylate monomers and their copolymerization with a sulfopropylbetaine (SPB) methacrylate yielded well-defined (co)polymers with low dispersities 1.13 ≤ ĐM ≤ 1.23 at monomer conversions of 75–92%. For a series of SBB methacrylate homopolymers with increasing degrees of polymerization from 66–186 measured upper critical solution temperature (UCST) cloud points increased from 27–77 °C. Cloud points of statistical SPB-SBB copolymers with similar degrees of polymerization, but varying molar compositions, increased linearly with SBB content offering a simple means of UCST tuning. Additionally, novel SBB acrylamide homo- and copolymers were prepared by postpolymerization modification of poly(pentafluorophenyl acrylate) with an SBB-functional amine and in mixtures with benzylamine as a hydrophobic modifier. In all cases, the SBB (co)polymers had significantly higher UCSTs than their more common SPB counterparts, greatly extending the temperature range of tuneable UCST transitions and making the investigated SBB (co)polymers advantageous for exploiting their ‘smart’ behaviour. In this respect, combining SBB functionality with hydrophobic benzylacrylamide comonomers is presented as a simple means of increasing the maximum salt concentration at which UCST behaviour (which shows an antipolyelectrolyte effect) can be observed, enabling UCST transitions in aqueous solutions containing a physiological concentration (9 g L−1) of NaCl.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Emerging Investigators

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...