Preparation of sodium trimetaphosphate and its application as an additive agent in a novel polyvinylidene fluoride based gel polymer electrolyte in lithium sulfur batteries
Abstract
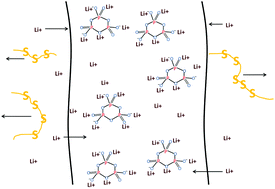
Six-membered cyclic sodium trimetaphosphate with strong electronegativity and an excellent capability of chelating metal cations was prepared via a convenient calcining method and used as an additive agent in a PVDF-based gel polymer electrolyte membrane for lithium sulfur batteries after being ion-exchanged with Li+ cations. The membrane and its application in lithium sulfur batteries were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), thermogravimetry (TG), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), linear sweep voltammetry (LSV), charge–discharge test, cyclic voltammetry (CV), and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS). Results show that this novel gel polymer electrolyte exhibits a high ionic conductivity of 2–4 mS cm−1 between 17 and 76 °C and has promising characteristics for use in lithium sulfur batteries. The “shuttle effect”, which is the critical issue for lithium sulfur batteries, is restrained because of using the gel polymer electrolyte with the trimetaphosphate added to it.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...