Water-dispersible cationic polyurethanes containing pendant trialkylphosphoniums†
Abstract
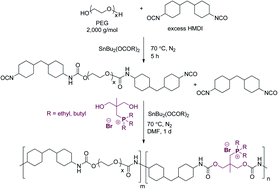
Novel trialkylphosphonium ionic liquids chain extenders enabled the successful synthesis of poly(ethylene glycol)-based, cationic polyurethanes with pendant phosphoniums in the hard segments (HS). Aqueous size exclusion chromatography (SEC) confirmed the charged polyurethanes, which varied the phosphonium alkyl substituent length (ethyl and butyl) and cationic HS content (25, 50, 75 mol%), achieved high absolute molecular weights. Dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA) demonstrated the triethylphosphonium (TEP) and tributylphosphonium (TBP) polyurethanes displayed similar thermomechanical properties, including increased rubbery plateau moduli and flow temperatures. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) emphasized the significance of ion–dipole interaction on hydrogen bonding. Atomic force microscopy (AFM), small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS), and wide-angle X-ray diffraction (WAXD) supported microphase separated morphologies in the trialkylphosphonium polyurethanes, despite the presence of ionic interactions. Sorption isotherm experiments revealed the TEP polyurethane exhibited the highest water vapor sorption profile compared to the TBP, which displayed similar water sorption profiles to the noncharged analogue. The phosphonium polyurethanes displayed significantly improved tensile strain; however, lower tensile stress of the TEP polyurethane was presumably due to absorbed water. In addition to physical characterizations, we also explored the trialkylphosphonium polyurethanes as nucleic acid delivery vectors. The phosphonium polyurethanes bound DNA at low charge ratios, and the polyplexes exhibited enhanced colloidal stability under physiological salt conditions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...