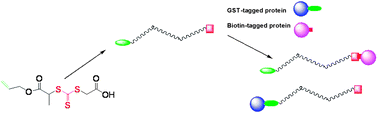
α-Glutathione (GSH), ω-biotin functionalized poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAAm) was synthesized via reversible addition–fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization using a new R-group allyl functionalized trithiocarbonate chain transfer agent (CTA) and thiol–ene reactions. GPC and 1H NMR results indicated that the allyl group had no adverse effect on the RAFT-controlled polymerization of NIPAAm and PEG-A, and the new CTA could efficiently control the polymerizations. Employing radical thiol–ene and Michael addition reactions, heterotelechelic α-allyl, ω-carboxylic acid-PNIPAAm was first aminolyzed in the presence of maleimide-modified biotin and subsequently reacted with GSHvia radical thiol–ene addition to yield α-GSH, ω-biotin functionalized PNIPAAm. Glutathione S-transferase (GST) and streptavidin (SAv) were coupled in solution with heterofunctional PNIPAAmvia bioaffinity interactions. Separately, α-GSH, ω-biotin functionalized PNIPAAm was further shown to bind GST-tagged Rac1, a potential cancer marker, and biotin-tagged bovine serum albumin (BSA).
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...