XPS studies on dispersed and immobilised carbon nitrides used for dye degradation
Abstract
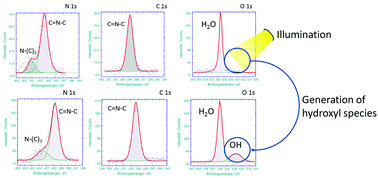
Liquid phase adsorption is a common technique in waste water purification. However, this process has some downsides. The removal of environmentally harmful contaminants from organic liquids by adsorption produces secondary waste which has to be treated afterwards. The treatment can be e.g. high temperatures or a landfill. Photocatalysts such as CN6 can remove the dye under light irradiation but most times they have to be separated afterwards. Immobilisation of these photocatalysts can be one way to address this problem. The resulting photocatalyst layers were analysed in operando by near-ambient pressure XPS. This enabled us to detect the active species, i.e. oxygen radicals, at the surface, responsible for the dye degradation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...