Stereoselective self-aggregation of synthetic zinc 31-epimeric bacteriochlorophyll-d analogs possessing a methylene group at the 132-position as models of green photosynthetic bacterial chlorosomes†
Abstract
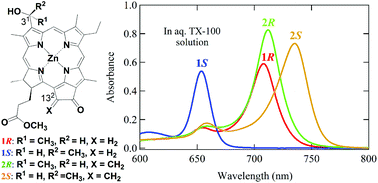
Zinc bacteriochlorophyll-d analogs possessing a methylene group at the 132-position were prepared by chemical modification of naturally occurring chlorophyll-a. The synthetic 31-epimers were successfully separated by reverse phase HPLC to give diastereomerically pure samples. The stereochemistry of the chiral C31-center in the separated bacteriochlorophyll-d analogs was determined by HPLC analysis of the authentic stereoisomers prepared stereospecifically. Both the epimers were monomeric in tetrahydrofuran to give sharp absorption bands, while they self-aggregated to form chlorosomal oligomers with red-shifted bands in an aqueous Triton X-100 micelle solution. The resulting large oligomers deaggregated by addition of Triton X-100 to give monomeric species. Their aggregation and deaggregation were dependent on the 31-stereochemistry, indicating that each epimer produced self-aggregates that were supramolecularly different. The substitution with the 132-methylene group enhanced their self-aggregation abilities and the stability of their resulting self-aggregates.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...