A theoretical study of 5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-6-hydroxymethylpterin: insight into intrinsic photoreceptor properties of 6-substituted tetrahydropterins†
Abstract
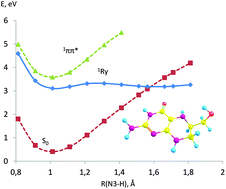
Tetrahydropterins are essential biological cofactors, which play a crucial role in DNA and RNA syntheses, NO synthesis, hydroxylation of aromatic amino acids, etc. In the last few years, it has been shown that 6-substituted “unconjugated” tetrahydropterins can also play a photoreceptor chromophoric role in plants and cyanobacteria. However, the nature of the initial light signal transduction act in which H4pterins participate is unknown. Our quantum chemical calculations have shown the possibility of the fast internal conversion of excited states of H4pterins. The potential energy surface scan along the 1ππ* state shows no energy barrier leading to 1ππ*/S0 conical intersection, this explains the absence of fluorescence for H4pterins. Other trajectories of the internal conversion relate to the stretching vibrations of the N–H bonds of the pyrimidine ring for the Rydberg state. The presence of several trajectories of nonradiative quenching of the photoexcited singlet states provides the photostability of the molecule. It was demonstrated for the first time that the nature of the excited states of H4pterins is similar to the nature of the excited states of guanine.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...