Investigations on the photochromic properties of 2,6-bis(5-bromo-2-hydroxybenzylidene)cyclohexanone†
Abstract
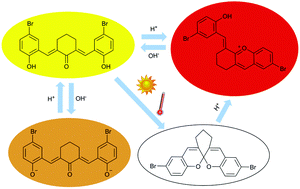
The network of chemical reactions of 2,6-bis(5-bromo-2-hydroxybenzylidene)cyclohexanone (BHBC) when subjected to light and different pH values has been investigated. The pH dependent species involved in the chemical network have been identified and characterized by NMR and UV-VIS spectroscopy. Direct pH jumps were carried out by adding a strong acid to equilibrated solutions of trans-chalcone (Ct) forming the flavylium cation which was stable only under extremely acidic conditions (pH < 0.5). The single crystal X-ray study and NMR analysis has confirmed the structure of the new flavylium cation. In the case of a reverse pH jump, the Ct species interconverted instantaneously into deprotonated trans-chalcone (Ct2−) around pH 12. A new colorless compound 3,11-dibromo-7,8-dihydro-6H-chromeno[3,2-d]xanthene (B–B) isolated from the equilibrated solution of trans-chalcone species in methanol after long periods of time (100 h) under dark conditions has been isolated and fully characterized by NMR and X-ray diffraction. The rate of the reaction increased when the solution of trans-chalcone was exposed to light and the total conversion of Ct into the spiropyran-like compound (B–B) was achieved in about 30 minutes. The B–B form was stable under neutral and basic conditions, while at low pH values it converts into a cationic AH+ form.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...