Topical treatment of green tea polyphenols emulsified in carboxymethyl cellulose protects against acute ultraviolet light B-induced photodamage in hairless mice
Abstract
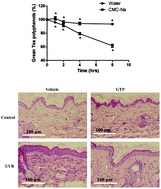
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation causes skin injury and inflammation resulting in impaired immune response and increased risk of skin cancer. It has been shown that green tea polyphenols (GTPs) enhanced intracellular antioxidant defense and promoted the downregulation of proapoptotic genes, and they could be used to protect against the damage induced by UV irradiation. However, the high instability and poor bioavailability of GTPs impose restrictions on their potential pharmacological use. Here we show that carboxymethyl cellulose sodium (CMC-Na) had a stabilizing effect on GTPs under aqueous conditions and topical application of GTPs (emulsified in CMC-Na) had a strong photoprotective effect against acute UVB induced photodamage in uncovered (Uncv) hairless mice skin. After 8 h of incubation at 50 °C with CMC-Na, a percentage i.e. 93% of GTPs was preserved, while in the absence of CMC-Na, a percentage of only 61% was preserved. Topical treatment of emulsified GTPs effectively inhibited acute UVB-induced infiltration of inflammatory cells, increase of skin thickness, oxidative stress such as depletion of antioxidant enzymes and lipid oxidation, and induced nuclear accumulation of Nrf2 in the mice skin. We also discovered the ability of GTPs to simultaneously trigger accumulation of nuclear Nrf2 and export of nuclear Bach1. Altogether, our findings reinforced the putative application of GTPs in the prevention/minimization of the deleterious effects of UV on the skin.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...