Ultraviolet-activated persulfate oxidation of methyl orange: a comparison between artificial neural networks and factorial design for process modelling
Abstract
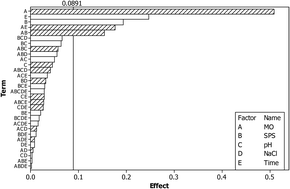
In this work, the degradation of the azo dye methyl orange in model aqueous solutions by UVC light-induced persulfate oxidation was studied. Five operating parameters that may influence the decolorization kinetics were evaluated, namely, methyl orange (MO) (5–50 mg L−1) and sodium persulfate (SPS) (50–150 mg L−1) concentration, reaction time (up to 60 min), (un-buffered) solution pH (3–9) and the addition of NaCl (0–500 mg L−1). The process was simulated, applying and comparing two methodologies, namely two-level factorial design and an artificial neural network (ANN). It was found that MO concentration is the most influential parameter, followed by the reaction time and SPS concentration, while the effects of solution pH and the addition of sodium chloride are statistically less significant; this order of significance was predicted by both methodologies. The ANN can simulate the process more accurately (i.e. in terms of R2, mean square error (MSE) and residuals) than factorial design, although it needs significantly larger sets of data and longer computational time.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Solar Chemistry and Photocatalysis - environmental applications

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...