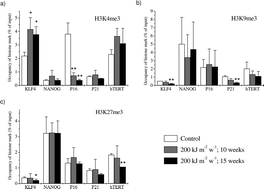
UVA-radiation (315–400 nm) has been demonstrated to be capable of inducing DNA damage and is regarded as a carcinogen. While chromosomal aberrations found in UVA-irradiated cells and skin tumors provided evidence of the genetic involvement in UVA-carcinogenesis, its epigenetic participation is still illusive. We thus analysed the epigenetic patterns of 5 specific genes that are involved in stem cell fate (KLF4, NANOG), telomere maintenance (hTERT) and tumor suppression in cell cycle control (P16INK4a, P21WAFI/CIPI) in chronically UVA-irradiated HaCaT human keratinocytes. A striking reduction of the permissive histone mark H3K4me3 has been detected in the promoter of P16INK4a (4-fold and 9-fold reduction for 10 and 15 weeks UVA-irradiated cells, respectively), which has often been found deregulated in skin cancers. This alteration in histone modification together with a severe promoter hypermethylation strongly impaired the transcription of P16INK4a (20-fold and 40-fold for 10 weeks and 15 weeks UVA-irradiation, respectively). Analysis of the skin tumor-derived cells revealed the same severe impairment of the P16INK4a transcription attributed to promoter hypermethylation and enrichment of the heterochromatin histone mark H3K9me3 and the repressive mark H3K27me3. Less pronounced UVA-induced epigenetic alterations were also detected for the other genes, demonstrating for the first time that UVA is able to modify transcription of skin cancer associated genes by means of epigenetic DNA and histone alterations.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...