The suppression of immunity by ultraviolet radiation: UVA, nitric oxide and DNA damage
Abstract
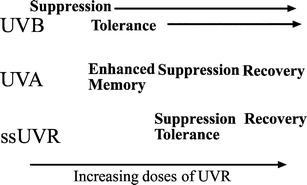
We have examined the mechanism by which solar-simulated ultraviolet radiation (ssUV) suppresses memory immunity to nickel in allergic humans. In initial studies, we used inbred mice to determine the contribution of different wavebands to sunlight-induced immunosuppression. We found that low dose UVA can enhance memory, medium dose UVA (half the amount in one minimum erythemal dose of ssUV) is immunosuppressive, but higher doses protect from UVB. This is genetically dependent, as it is not observed in all mouse strains. UVA caused a similar dose-related change in recall immunity in humans. ssUV dose responses determined the limits of protection provided by sunscreens from immunosuppression in humans. Immune protection factors calculated from these data correlated with UVA protection, but not with sun protection factor, showing that in commercial sunscreens that provide good UVB protection, UVA protection limits prevention of immunosuppression.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 10th Congress of the European Society for Photobiology

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...