Photorepair activity and protective compounds in two freshwater zooplankton species (Daphnia menucoensis and Metacyclops mendocinus) from Patagonia, Argentina
Abstract
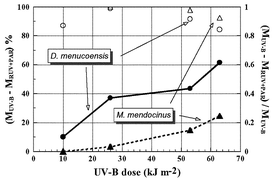
The impact of ultraviolet-B radiation (UV-B, 280–315 nm) on the cladoceran Daphnia menucoensis Paggi and the copepod Metacyclops mendocinus
(Wierzejski) was determined in experiments designed to evaluate the effectiveness of the photorepair mechanism and the role of UV-absorbing compounds. In both species UV-B caused significant mortality at doses of ∼40 kJ m−2 or higher. At lower UV-B doses, however, no significant mortality was detected in M. mendocinus; moreover, this species seems to have a threshold below which no UV-B induced mortality is determined. D. menucoensis, on the other hand, was very sensitive to UV-B, and significant mortality of 15%
(p < 0.05) was observed when doses were as low as 10 kJ m−2. Both species showed high efficiency for photorepairing UV-B-induced damage to the DNA molecule, with a significant decrease of mortality when the species were exposed to visible radiation, PAR (55 W m−2), in addition to UV-B. The higher resistance of M. mendocinus to UV-B as compared to that of D. menucoensis might be also related to the presence of

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...