The formation of neutral CCC and its radical cation from the CCC radical anion in the gas phase. A joint experimental and theoretical study
Abstract
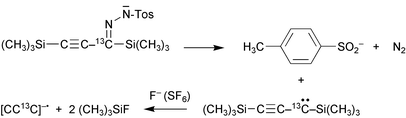
The ![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) C13C(
C13C(![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) NNHSO2C6H4-p-CH3)Si(CH3)3] with HO−/F− in the ion source of a mass spectrometer. The stable anion undergoes vertical two-electron
NNHSO2C6H4-p-CH3)Si(CH3)3] with HO−/F− in the ion source of a mass spectrometer. The stable anion undergoes vertical two-electron

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...