Quantum topological molecular similarity. Part 4.† A QSAR study of cell growth inhibitory properties of substituted (E)-1-phenylbut-1-en-3-ones
Abstract
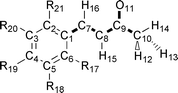
In this paper we apply a novel method called ‘quantum topological molecular similarity’ (QTMS) to a QSAR of antitumor activity of fifteen (E)-1-phenylbut-1-en-3-ones. The electronic structure of the molecules is compactly and accurately described by a set of topological descriptors drawn from ab initio wave functions. These descriptors consist of quantum mechanical properties evaluated at so-called bond critical points (BCP). These are special saddle points in the electron density located inside the molecule, roughly between two bonded nuclei. We use a partial least squares (PLS) analysis to obtain a valid regression with r2
= 0.91 and q2
= 0.86. QTMS highlights a region in the molecule comprising the active center of a

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...