Novel near-infrared fluorescent probe with a large Stokes shift for sensing hypochlorous acid in mitochondria†
Abstract
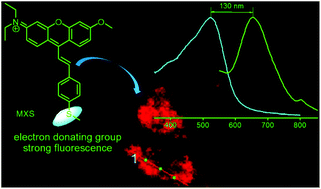
Hypochlorous acid (HOCl) plays a crucial role in various physiological and pathological processes. However, it is still a challenge to design a xanthene-based near-infrared (NIR) fluorescent probe with a large Stokes shift for sensing HOCl. In this work, a novel mitochondria-targeted fluorescent probe, MXS, with a large Stokes shift based on a xanthene-hemicyanine dyad structure, has been successfully designed and synthesized for the specific detection of HOCl. Gratifyingly, the peak-to-peak Stokes shift of MXS was found to be 130 nm, which was obviously larger than those of conventional rhodamine dyes and most reported xanthene-based hypochlorous acid probes. As expected, MXS exhibited high selectivity, high sensitivity, and fast response time (30 s) for the detection of HOCl via a specific HOCl-promoted intramolecular charge transfer process. The detection limit of MXS for HOCl is calculated to be as low as 72 nM, enabling its use within the physiological concentration range of HOCl (5–25 μM). Importantly, MXS is able to permeate cell membranes and accumulate in the mitochondria, which is convenient for monitoring the variation of hypochlorous acid concentration in the mitochondria of living cells.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...