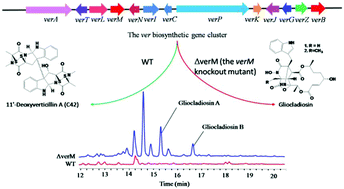
The disruption of verM activates the production of gliocladiosin A and B in Clonostachys rogersoniana†
Abstract
Gliocladiosin A (1) and B (2), two dipeptides conjugated with macrolides, were identified from a verM disruption mutant of the Cordycep-colonizing fungus Clonostachys rogersoniana. The structures and absolute configurations of 1 and 2 were determined on the basis of spectroscopic data analysis, including MS, NMR, CD and X-ray diffraction. A biogenetic pathway for 1 and 2 was proposed. These two compounds showed moderate antibacterial effects.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...