A new mechanism for internal nucleophilic substitution reactions†
Abstract
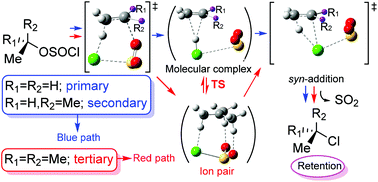
A new mechanism for the classic internal nucleophilic substitution reactions SNi by means of computational studies in the gas-phase, DCM and acetonitrile is reported. Despite the importance of the SNi mechanism, since the mid-1990s this mechanism has remained unexplored. This study focused mainly on the comparison between the mechanisms postulated to date for the SNi reactions and a new mechanism suggested by us that fits better the experimental observations. This comparative study has been applied to the conversion of ethyl, neopentyl, isopropyl and tert-butyl chlorosulfites into the corresponding alkyl chlorides. This new mechanism occurs through two transition structures. For primary and secondary substrates, the first transition structure is a 6-center syn-rearrangement of the alkanesulfonyl chloride that produces the corresponding olefin by simultaneous expulsion of HCl and SO2. The olefin, HCl and SO2 form a molecular complex. The final syn-addition of HCl to the olefin leads to alkyl chloride with the retention of configuration. For tertiary substrates, a variation of the previous mechanism is postulated with the intervention of contact ion pairs. It is of great importance to emphasize that this new mechanism is able to explain some experimental observations such as the presence of olefins in these types of reactions and the low reactivity of some systems such as neopentyl chlorosulfite. Our results pave the way to a new mechanistic perspective in similar reactions which will need further studies and validation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...