Enzymatic monoesterification of symmetric diols: restriction of molecular conformations influences selectivity†
Abstract
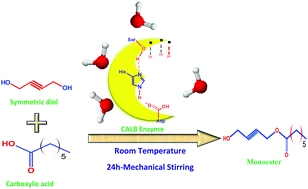
We have experimentally demonstrated that by ‘locking’ the molecular conformation through the introduction of a double or triple bond in the center of a symmetric diol, enzymatic monoesterification can be achieved selectively. The enzyme Candida antarctica lipase B, generally used for the transesterification of diols, can be effectively used for the monoesterification of symmetrical diols in an unbuffered system also. By varying the chain length of a carboxylic acid moiety, we have established that optimum selectivity and efficiency can be achieved in the range of 4.8 to 5.0 pKa values. Selectivity can be improved up to 98.75% for a monoester in an overall 73% yield (mixture of a monoester and a diester) when but-2-yne-1,4-diol reacted with hexanoic acid. Water, a by-product, provides an interfacial environment for the enzyme to work in the organic reaction medium. The uniqueness of the reported monoesterification protocol is that it involves only the mechanical stirring of the reaction mixture at room temperature in the presence of the enzyme for 24 h. High percentage yield with selectivity for a monoester, easier product isolation and overall, environmental sustainability are added advantages. The synthesized monoesters are characterized by using HNMR and high resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...