Polymeric prodrug combination to exploit the therapeutic potential of antimicrobial peptides against cancer cells†
Abstract
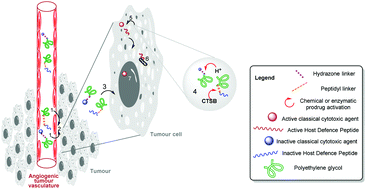
Antimicrobial Peptides (AMPs) have unique anticancer properties, but their clinical application is currently limited by an inadequate margin of safety. A prodrug strategy associated with a combination therapy approach could address this limitation by increasing their therapeutic index and their efficacy. Accordingly, the first targeted anticancer polymeric prodrug candidates of AMPs, intended for combination therapy with another polymeric prodrug of an approved antineoplastic agent (doxorubicin), were synthesized as either a PEG-based dual-release prodrug or two individual pegylated prodrugs. The latter are based on a cathepsin B-labile peptide linker and an acid-sensitive acyl hydrazone bond for the AMP and doxorubicin prodrugs, respectively. Anticancer activities and toxicity differentials achieved with the free peptide and its polymer conjugates against ovarian, cancer and non-malignant, cells, indicate that protease-dependent reversible pegylation could be implemented to increase the therapeutic indices of AMPs in cancer therapy. The results obtained also show that this approach can be developed if the releasable PEG linker can be optimised to conciliate the attributes and restrictions of pegylation against proteases. In addition, combination of the polymeric prodrugs of the AMP and of doxorubicin provides additive antitumor effects which could be exploited to enhance the efficacy of the AMP candidate.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...