ONIOM calculations on serotonin degradation by monoamine oxidase B: insight into the oxidation mechanism and covalent reversible inhibition†
Abstract
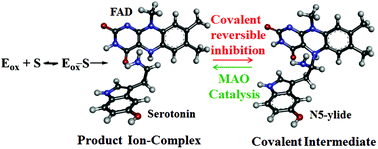
Monoamine oxidase (MAO) is an enzyme which catalyzes the oxidation of neurotransmitter amines and regulates their level. There are two forms of the enzyme with 70% similarity, known as MAO-A and MAO-B. MAO inhibitors are used in the treatment of neurological disorders such as depression, Parkinson's and Alzheimer's diseases. Therefore, understanding the chemical steps of MAO catalyzed amine oxidation is crucial for rational drug design. However, despite many experimental studies and recent computational efforts in the literature, the amine oxidation mechanism by MAO enzymes is still controversial. The polar nucleophilic mechanism and hydride transfer mechanisms are under debate in recent QM/MM studies. In this study, the serotonin oxidation mechanism by MAO was explored via the ONIOM (QM : QM) methodology at the M06-2X/6-31+G(d,p):PM6 level. A modified MAO mechanism involving a covalent reversible inhibition step via formation of flavin N5 ylide was proposed. This mechanism can be used to modulate the potency and reversibility of novel mechanism-based covalent inhibitors by intelligent modifications of the structure of the inhibitors. NBO donor–acceptor analysis confirms that the rate-determining αC–H cleavage step is a hybrid of hydride and proton transfer where hydride transfer dominates over the proton transfer. The functional role of covalent FAD was also investigated by calculating the activation energy of noncovalent FAD models where a 22 fold decrease in the rate of catalysis was predicted. Geometrical features imply that the function of the covalent bond in FAD might be to maintain the correct geometry and conformation for a more efficient catalysis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...