Stereoselective Pd-catalyzed etherification and asymmetric synthesis of furanomycin and its analogues from a chiral aziridine†
Abstract
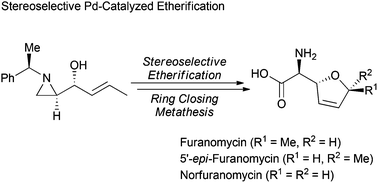
A chiral aziridine was utilized for the synthesis of the anti-bacterial natural amino acid L-(+)-furanomycin, and its analogues including 5′-epi-furanomycin and norfuranomycin. Key steps of this synthesis are the stereoselective Pd-catalyzed etherification for diallyl ethers and ring closing metathesis.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...