Design, synthesis, and kinetic analysis of potent protein N-terminal methyltransferase 1 inhibitors†
Abstract
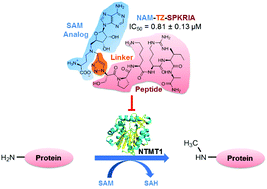
The protein N-terminal methyltransferase 1 (NTMT1) methylates the α-N-terminal amines of proteins. NTMT1 is upregulated in a variety of cancers and knockdown of NTMT1 results in cell mitotic defects. Therefore, NTMT1 inhibitors could be potential anticancer therapeutics. This study describes the design and synthesis of the first inhibitor targeting NTMT1. A novel bisubstrate analogue (NAM-TZ-SPKRIA) was shown to be a potent inhibitor (Ki = 0.20 μM) for NTMT1 and was selective versus protein lysine methyltransferase G9a and arginine methyltransferase 1. NAM-TZ-SPKRIA was found to exhibit a competitive inhibition pattern for both substrates, and mass spectrometry experiments revealed that the inhibitor substantially suppressed the methylation progression. Our results demonstrate the feasibility of using a triazole group to link an S-adenosyl-L-methionine analog with a peptide substrate to construct bisubstrate analogues as NTMT1 potent and selective inhibitors. This study lays a foundation to further discover small molecule NTMT1 inhibitors to interrogate its biological functions, and suggests a general strategy for the development of selective protein methyltransferase inhibitors.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...