Bleomycin-induced trans lipid formation in cell membranes and in liposome models†
Abstract
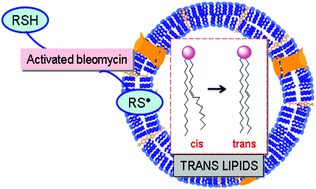
Cell cultures of NTera-2 cells incubated with bleomycin and liposomes as biomimetic models of cell membranes were used for examining some novel aspects of drug–metal induced reactivity with unsaturated lipids under oxidative conditions. In cell cultures, bleomycin was found for the first time to cause the formation of trans fatty acids. The chemical basis of this transformation was ascertained by liposome experiments, using bleomycin–iron complexes in the presence of thiol as a reducing agent that by incubation at 37 °C gave rise to the thiyl radical-catalysed double bond isomerisation of membrane phospholipids. The effect of oxygen and reagent concentrations on the reaction outcome was studied. An interesting scenario of free radical reactivity is proposed, which can be relevant for understanding the role of membrane lipids in antitumoral treatments and drug carrier interaction.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...