Amino acid-linked porphyrin-nitroimidazole antibiotics targeting Porphyromonas gingivalis†
Abstract
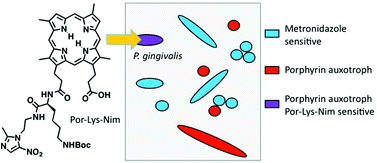
The periodontal pathogen Porphyromonas gingivalis requires porphyrin supplementation for growth. Previously, in order to inhibit P. gingivalis growth, we synthesised very effective ‘Trojan horse’ ester and amide-linked deuterporphyrin-nitroimidazole (DPIX-Nim) adducts that exploited this requirement to transport metronidazole-derived antibiotics with excellent antimicrobial selectivity and recognition by the HA2 porphyrin binding site. Herein, in the context of developing topical agents to target P. gingivalis, L-amino acids are incorporated into adducts as linkers to improve uptake. Ten 13- and 17-propionic amide regioisomers of L-amino acid-linked deuterporphyrin-nitroimidazole adducts were synthesised using a peptide coupling approach. DPIX-Lys regioisomers without attached nitroimidazole were also synthesised as comparison compounds. All the porphyrin adducts bound (Kd50 7 to 20 nM) to a recombinant HA2 receptor with similar binding affinity to haem, except the lysine-proline linked DPIX-Lys(Boc)Pro-Nim adducts (Kd50 300 nM) and the DPIX-Lys(Nim)-Nim adducts (Kd50 200 nM), both of which have large appended groups. DPIX-Lys(Boc)-Nim, DPIX-Lys(OH)-Nim, and DPIX-Pro-Nim adducts were shown to be very effective against P. gingivalis. DPIX-Lys(Boc)Pro-Nim adducts and DPIX-Lys(Nim)-Nim adducts showed weak activity. Importantly, DPIX-Lys(Boc)-Nim adducts were selective for P. gingivalis and, unlike metronidazole, did not kill a range of other anaerobic bacteria isolated from the human gastrointestinal tract.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...