Selective recognition of anionic cell membranes using targeted liposomes coated with zinc(ii)-bis(dipicolylamine) affinity units†
Abstract
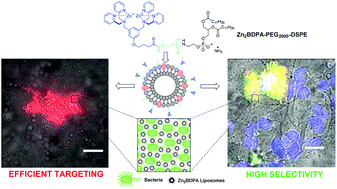
Zinc(II)-bis(dipicolylamine) (Zn2BDPA) coated liposomes are shown to have high recognition selectivity towards vesicle and cell membranes with anionic surfaces. Robust synthetic methods were developed to produce Zn2BDPA-PEG-lipid conjugates with varying PEG linker chain length. One conjugate (Zn2BDPA-PEG2000-DSPE) was used in liposome formulations doped with the lipophilic near-infrared fluorophore DiR. Fluorescence cell microscopy studies demonstrated that the multivalent liposomes selectively and efficiently target bacteria in the presence of healthy mammalian cells and cause bacterial cell agglutination. The liposomes also exhibited selective staining of the surfaces of dead or dying human cancer cells that had been treated with a chemotherapeutic agent.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Supramolecular Chemistry in Water

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...