An intracellularly activatable, fluorogenic probe for cancer imaging†
Abstract
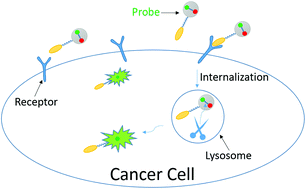
A newly designed, dual-functional probe based on intracellular activation has been successfully developed for the detection of cancer cells. The probe is nearly non-fluorescent in buffer due to its highly efficient FRET quenching, but it can be specifically activated with dramatic fluorescence enhancement upon intracellular cathepsin B cleavage in target cancer cells after selective internalization via folate receptor-dependent endocytosis. Therefore, this probe enables “turn-on” visualization of cancer cells with desirable specificity and contrast enhancement. This targeted, intracellularly activatable probe exhibits low fluorescence-quenched background when compared with “always-on” probes and avoids non-specific activation by non-specifically expressed enzymes in normal tissue, which normally occurs when using common “turn on” probe design strategies. Therefore, this probe can be potentially applied in intraoperative inspection during clinical cancer surgery with higher contrast and sensitivity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...