Effect of H-bonding and complexation with metal ions on the π-electron structure of adenine tautomers†‡
Abstract
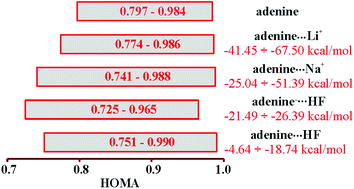
Influence of H-bonding and interactions with metals via complexation (probed by HF, F−, Li+ and Na+) on structural and π-electronic changes in four of the most stable amino adenine tautomers has been studied in the gas phase using the B3LYP/6-311++G(2d,2p) computational level. It has been found that the presence of the amino group in adenine increases its energetic sensitivity to structural changes caused by tautomeric effects as compared to its analogue deprived of this group (purine). Furthermore, its shape depends not only on tautomerism but also on intermolecular interactions. The observed variability of its pyramidalizations caused by H-bonding indicates the dramatic changes of electron donating/accepting properties of –NH2 as a substituent, which results in a variation of aromaticity of particular rings in adenine tautomers. Bifurcated coordination of metal cations by two nitrogen atoms of adenine is also an important factor influencing aromaticity. The overall range of H-bond strengths is between −4.64 and −26.39 kcal mol−1, whereas energies for Li+ and Na+ complexes are in the ranges −41.45 to −67.50 and −25.04 to −51.39 kcal mol−1, respectively. However, the highest aromaticity changes, expressed by the HOMA index, have been found to be about 24% of the HOMA scale for all types of complexes depending on the location of the intermolecular interaction.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...