Investigating the oxidation of alkenes by non-heme iron enzyme mimics†
Abstract
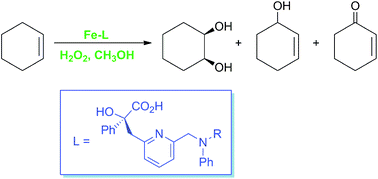
Iron is emerging as a key player in the search for efficient and environmentally benign methods for the functionalisation of C–H bonds. Non-heme iron enzymes catalyse a diverse array of oxidative chemistry in nature, and small-molecule complexes designed to mimic the non-heme iron active site have great potential as C–H activation

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...