γ-Glutamyl transpeptidase acylation with peptidic substrates: free energy relationships measured by an HPLC kinetic assay†
Abstract
γ-Glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT, EC 2.3.2.2) is a highly glycosylated heterodimeric enzyme linked to the external cellular membrane that catalyzes the hydrolysis of
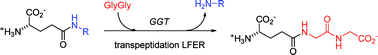

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...