The ammonia-free partial reduction of substituted pyridinium salts
Abstract
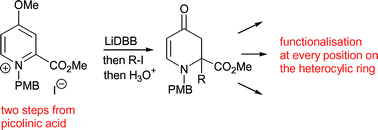
This paper reports a study into the partial reduction of N-alkylpyridinium salts together with subsequent elaboration of the intermediates thus produced. Activation of a pyridinium salt by placing an ester group at C-2, allows the addition of two electrons to give a synthetically versatile enolate intermediate which can be trapped with a variety of electrophiles. Furthermore, the presence of a 4-methoxy substituent on the pyridine nucleus enhances the stability of the enolate reaction products, and hydrolysis in situ gives stable dihydropyridone derivatives in good yields. These versatile compounds are prepared in just three steps from picolinic acid and can be derivatised at any position on the ring, including nitrogen when a p-methoxybenzyl group is used as the N-activating group on the pyridinium salt. This publication describes our exploration of the optimum reducing conditions, the most appropriate N-alkyl protecting group, as well as the best position on the ring for the methoxy group. Electrochemical techniques which mimic the synthetic reducing conditions are utilised and they give clear support for our proposed mechanism of reduction in which there is a stepwise addition of two electrons to the heterocycle, mediated by di-tert-butylbiphenyl (DBB). Moreover, there is a correlation between the viability of reduction of a given heterocycle under synthetic conditions and its electrochemical response; this offers the potential for use of electrochemistry in predicting the outcome of such reactions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...