Ultrasmall Prussian blue nanoparticles attenuate UVA-induced cellular senescence in human dermal fibroblasts via inhibiting the ERK/AP-1 pathway
Abstract
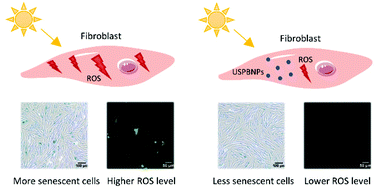
Ultraviolet A (UVA) irradiation can induce cellular senescence and cause skin photoaging, which is mainly driven by the excessive production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Emerging studies have focused on new strategies for the prevention of skin photoaging. Ultrasmall Prussian blue nanoparticles (USPBNPs) demonstrate an intensive ability to scavenge ROS as nanozymes and exhibit great potential in the treatment of ROS-related diseases. Our goal was to investigate the anti-senescent role of USPBNPs against UVA-induced premature senescence in human dermal fibroblasts (HDFs). Our results showed that the activation of senescence-associated β-galactosidase (SA-β-gal) and the arrest of the cell cycle induced by UVA radiation in HDFs were significantly inhibited by pretreatment of USPBNPs (1 μg ml−1). Furthermore, USPBNPs downregulated the expression of DNA damage marker γH2AX and inhibited the secretion of senescence-associated secretory phenotypes (SASP) including IL-6, TNF-α and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs). In addition, we found that the antiphotoaging effect of USPBNPs involved the scavenging of ROS as well as the inhibition of the ERK/AP-1 pathway. In conclusion, USPBNPs exhibited great potential to become novel anti-photoaging agents by alleviating UVA-induced cellular senescence and thus delaying the process of skin photoaging.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...