Ionic charge distributions in silicon atomic surface wires†
Abstract
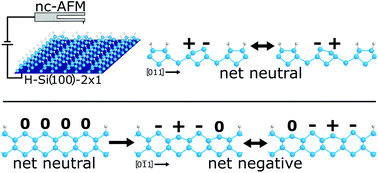
Using a non-contact atomic force microscope (nc-AFM), we examine continuous dangling bond (DB) wire structures patterned on the hydrogen terminated silicon (100)-2 × 1 surface. By probing the DB structures at varying energies, we identify the formation of previously unobserved ionic charge distributions which are correlated to the net charge of DB wires and their predicted degrees of freedom in lattice distortions. Performing spectroscopic analysis, we identify higher energy configurations corresponding to alternative lattice distortions as well as tip-induced charging effects. By varying the length and orientation of these DB structures, we further highlight key features in the formation of these ionic surface phases.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...