Nucleobase derived boron and nitrogen co-doped carbon nanosheets as efficient catalysts for selective oxidation and reduction reactions†
Abstract
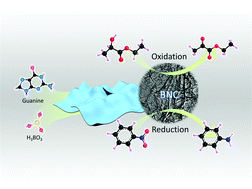
The search for active, stable and cost-efficient carbocatalysts for selective oxidation and reduction reactions could make a substantial impact on the catalytic technologies that do not rely on conventional metal based catalysts. Here we report a facile strategy for the synthesis of boron (B) and nitrogen (N) co-doped carbon nanosheets (BNC) by using biomolecule guanine as a carbon (C) and N source and boric acid as the B precursor. The whole synthesis process which leads to the formation of a two dimensional (2D) structure and mesoporosity with high surface areas is simple, metal-free and template-free. The as-synthesized carbon nanosheets possess a series of merits, such as relatively high specific surface area, satisfactory pore structure, enough structural defects, abundant B and N dopants as well as oxygen functional groups. The catalytic assessments demonstrate that the presented carbon catalyst is highly active and selective for the liquid phase oxidation of ethyl lactate to ethyl pyruvate and the reduction of nitrobenzene to aniline and outperforms other equivalent benchmarks. Control experiments confirm the importance of the B and N co-doping as well as the carbon matrix which benefit the electron transfer. The carbonyl group masking test indicates that carbonyl groups play an important role in both the selective oxidation and reductions. Given the diversity in the structure of the nucleobase moiety, they represent ideal building blocks for the catalyst-free and metal-free formation of 2D carbon architectures, only induced by hydrogen bonds. This B and N co-doped synthesis strategy provides guidance for the design of carbon-based catalysts for selective oxidation and reductions.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Celebrating 60 years of the Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...