A nanoplatform with tumor-targeted aggregation and drug-specific release characteristics for photodynamic/photothermal combined antitumor therapy under near-infrared laser irradiation†
Abstract
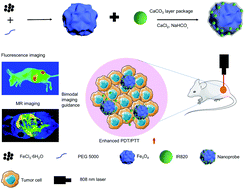
Due to their high biocompatibility, high spatial resolution, chromatographic capability, and adjustable size and morphology, magnetic nanoparticles have become the most promising nanomaterials for clinical application in noninvasive imaging and drug delivery for the treatment of malignant tumors. Herein, a novel magnetic nanoparticle coated with calcium carbonate was prepared and loaded with near-infrared drugs to be used as a multifunctional theranostic nanoplatform for the diagnosis and treatment of malignant tumors. Then, these drug-loaded nanoparticles were used for combined photodynamic/photothermal therapy by intravenous administration that was simultaneously guided by fluorescence/MR imaging. Due to the targeted induction of the external magnetic field and tumor response degradation of the calcium carbonate layer, the nanoprobe demonstrated excellent tumor targeting and greatly improved drug aggregation at the tumor site. Finally, single wavelength-mediated photothermal/photodynamic therapy was applied to liver cancer model mice, ultimately achieving an exciting antitumor therapeutic effect. This study may promote further exploration of nanoplatforms based on magnetic nanoparticles for clinical application in the treatment of malignant tumors.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...