Effect of oral exposure to titanium dioxide nanoparticles on lipid metabolism in Sprague-Dawley rats†
Abstract
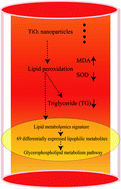
Ingestion of titanium dioxide nanoparticles (TiO2 NPs) via dietary and environmental exposure may pose health risks. The research about the potential effect of orally ingested nanoparticles on nutritional metabolism has been limited. We conducted an animal experiment to investigate the effect of oral exposure to TiO2 NPs on lipid metabolism in Sprague-Dawley rats. The rats were treated with TiO2 NPs (29 ± 9 nm) orally at doses of 0, 2, 10, 50 mg per kg bw daily for 90 days. Lipid metabolism is evaluated by biomarkers of serum lipids and lipidomics. TiO2 NPs caused a significant decrease of body weight in rats after exposure at doses of 10 and 50 mg kg−1 from the 8th to 13th week. The level of triglycerides (TG) decreased (0.398 ± 0.114 vs. 0.248 ± 0.058 nmol L−1) and the lipidomic signature changed significantly in the serum of rats treated with TiO2 NPs (50 mg kg−1). Sixty-nine well-matched lipophilic metabolites were differentially expressed and the glycerophospholipid metabolism pathway significantly changed. The concentrations of 32 metabolites including 19 kinds of phosphatidylcholines (PCs) increased and 37 metabolites including lysophosphatidylcholines (LysoPCs) and glycerophosphocholine decreased significantly in the TiO2 NP exposed group (50 mg kg−1). The accumulation of the lipid peroxidation product (malondialdehyde, MDA) and the decreased activity of the antioxidant enzyme SOD were observed and closely related to differential metabolites. In conclusion, orally ingested TiO2 NPs (50 mg kg−1) could have an impact on lipid metabolism, for which the strong induction of oxidative stress may be the main reason. The present study led to a better understanding of the oral toxicity of food-related TiO2 NPs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...