One-pot synthesis of Ln3+-doped porous BiF3@PAA nanospheres for temperature sensing and pH-responsive drug delivery guided by CT imaging†
Abstract
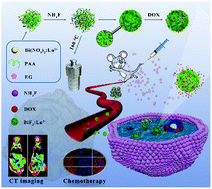
The design and synthesis of responsive inorganic nanocapsules have attracted intensive research interest in cancer treatment. The combination of non-invasive diagnosis and chemotherapy into a single theranostic nanoplatform is prospective in the biomedical field. In this work, a polyacrylic acid (PAA)-functionalized porous BiF3:Yb,Er nanocarrier was constructed via a straightforward one-pot solvothermal strategy. Compared with the undoped BiF3 sub-microspheres, the lanthanide ion (Ln3+) doping endowed the BiF3 material with a smaller size and increased BET specific surface area and pore volume, which make it suitable as a drug carrier. It was found that the synthesized nanomaterial could effectively relieve the side effects of doxorubicin (DOX) and exhibited pH-dependent DOX loading and release. Its satisfactory biocompatibility and efficient tumor inhibition were emphasized by a series of in vitro/in vivo experiments. In addition, the synthesized nanomaterial exhibited favorable CT contrast efficacy due to the excellent X-ray attenuation coefficient of Bi. Moreover, characteristic upconversion luminescence and temperature sensing in a wide temperature range were realized over the synthesized BiF3:Yb,Er sample. Therefore, carboxyl-functionalized BiF3:Yb,Er can be expected to be an ideal candidate in the fabrication of temperature sensing and multifunctional theranostic nanoplatforms.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...