Rediscovery of nylon upgraded by interactive biorenewable nano-fillers†
Abstract
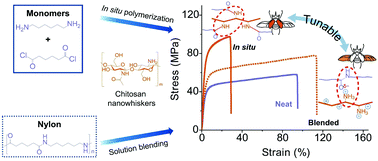
Inorganic nanomaterials can only stiffen nylon with a significant loss of its toughness and ductility. Furthermore, they are not eco-friendly. In this study, the facile tuning of nylon's mechanical properties from stiff to tough was achieved, using cellulose nanocrystals (CNC) and chitosan nanowhiskers (CSW) as biorenewable fillers. The interaction between the matrix and filler was controlled by varying the types of fillers and the employed processing methods, including in situ interfacial polymerization and post-solution blending. Particularly with CSW, the in situ-incorporated filler with a 0.4 wt% loading strengthened nylon and led to a 1.9-fold increase in its Young's modulus (2.6 GPa) and a 1.7-fold increase in its ultimate tensile strength (106 MPa), whereas the solution-blended filler with a 0.3 wt% loading toughened the polymer with a 2.1-fold increase (104 MJ m−3). Compared with inorganic nanocomposites, these interactive biofiller-nanocomposites are unrivaled in their reinforcing performance when normalized by filler content. This stiff-to-tough tuning trend is more pronounced in the CSW system than in the CNC system. Covalent polymer grafts on the amine surface of CSW enhanced interfacial interactions in the in situ method, whereas its cationic surface charges plasticized the polymer matrix in the blending method. This proteinaceous composite-mimicking all-organic nylon nanocomposite opens new possibilities in the field of reinforced engineering plastics.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...